Introduction
Electric power is the lifeblood of industrial systems, commercial facilities, and even home electronics. But not all power is created equal. In real-world electrical environments, power can be affected by noise, voltage disturbances, grounding issues, and safety risks. Clean, stable, and safe power matters — especially for sensitive equipment and human operators.
This is where the isolation transformer comes in.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explain what an isolation transformer is, how it works, why it’s used, the key benefits it provides, typical ratings and parameters, and where it’s commonly applied in modern electrical systems.
Whether you’re an engineer, facilities manager, system integrator, or a customer seeking reliable power solutions, this article will break the topic down clearly, practically, and from an application-focused perspective.
Click me!
What Is an Isolation Transformer?
At its core, an isolation transformer is a type of transformer that electrically separates its power input (primary winding) from its output (secondary winding) using magnetic coupling rather than a direct electrical connection.
While standard power transformers also provide basic isolation through separate windings, isolation transformers are specifically designed and optimized to:
-
prevent direct electrical contact between input and output circuits, and
-
provide Galvanic Isolation, meaning there is no conductive path for current to flow between the two sides except through magnetic induction.
Most isolation transformers are designed with a 1:1 voltage ratio, meaning the output voltage is the same as the input voltage. The purpose is not voltage conversion, but electrical separation, safety enhancement, and power quality improvement.
This simple yet critical design choice has major implications for electrical safety, noise control, system reliability, and equipment protection.
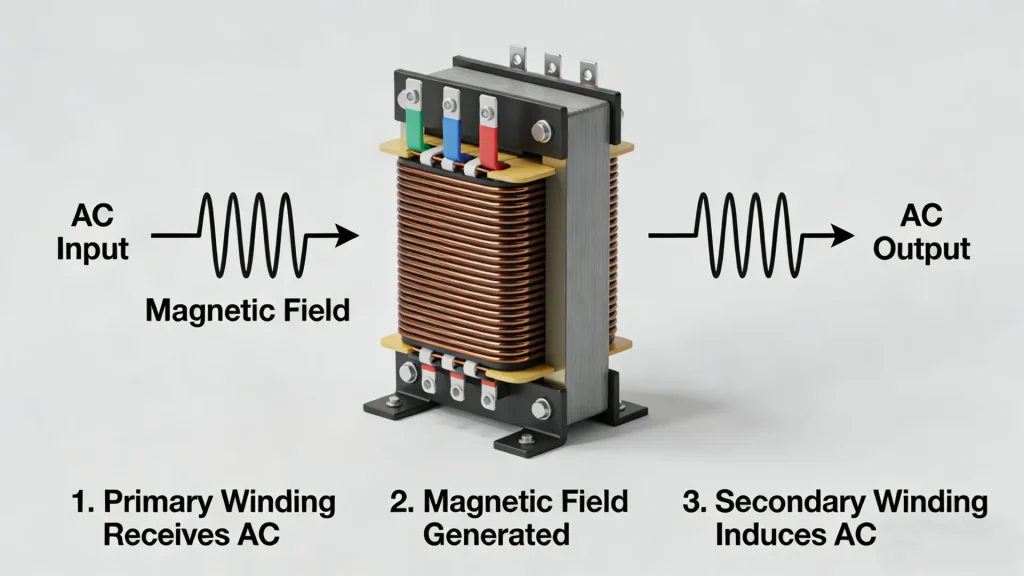
How Isolation Transformers Work
Isolation transformers operate on the same fundamental principle as other transformers: the transfer of electrical energy through electromagnetic induction.
Basic Operating Principle
Inside the transformer:
-
The primary winding receives AC power from the electrical supply.
-
This alternating current generates a continuously changing magnetic field in the transformer core.
-
The magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary winding.
-
No wires or conductors physically connect the primary and secondary windings — power is transferred only through the magnetic field.
Because of this no-contact design:
-
There is no direct electrical path for current to flow from the input side to the output side.
-
Any current delivered on the secondary side is created solely by magnetic induction.
-
The secondary circuit can be configured as floating, grounded, or center-tapped depending on system requirements.
Isolation transformers are commonly available in a wide range of power ratings, ranging from small control and instrumentation units (100 VA, 250 VA, 500 VA, 1 kVA, 2 kVA, and 5 kVA) to medium-capacity commercial systems (10 kVA, 15 kVA, 20 kVA, 30 kVA, and 50 kVA), and extending to large industrial power applications (75 kVA, 100 kVA, 150 kVA, 250 kVA, 300 kVA, 400 kVA, and 500 kVA or higher).
The Core Purpose — Safety and Protection
Electrical Shock Prevention
One of the most important reasons to use an isolation transformer is electrical safety.
Because the output circuit is electrically isolated from the input circuit’s ground reference:
-
There is no easy return path for fault current through a person touching the secondary side.
-
Accidental contact with a single live conductor on the isolated side is significantly less hazardous.
-
The risk of electric shock during maintenance, testing, or troubleshooting is reduced.
This safety advantage is especially valuable in medical environments, laboratories, test benches, repair stations, and industrial maintenance areas, where technicians may work directly on energized equipment.

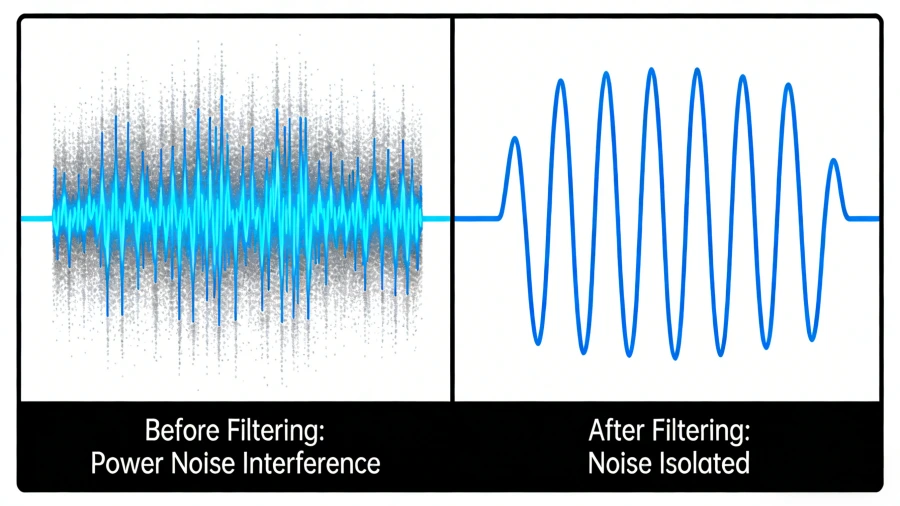
Power Quality — Noise and Interference Control
Isolation transformers also play a critical role in delivering clean, stable, and reliable power.
Blocking Electrical Noise
Because the primary and secondary circuits are not electrically connected:
-
Isolation transformers help block common-mode noise, which is noise that appears simultaneously on both conductors relative to ground.
-
They reduce the impact of ground potential differences between interconnected devices.
-
They help suppress electrical interference generated by variable frequency drives (VFDs), switching power supplies, and industrial machinery.
As a result, isolation transformers are widely used in systems that demand stable signal integrity and power quality, including:
-
High-fidelity audio and broadcast systems
-
Telecommunications and networking equipment
-
Sensitive industrial control panels
-
Measurement, instrumentation, and test systems
Surge and Transient Protection
Although isolation transformers are not designed to replace dedicated surge protection devices, their construction helps mitigate certain types of electrical disturbances.
-
Transformer windings naturally resist sudden changes in current.
-
High-frequency transients and fast voltage spikes are partially attenuated by the magnetic coupling process.
-
This reduces electrical stress on downstream equipment and extends component lifespan.
For critical installations, isolation transformers are commonly used together with surge protective devices (SPDs), transient voltage suppressors, and grounding systems to create a layered protection strategy.
Ground Loop Elimination
Ground loops occur when two or more devices are connected to different ground points while sharing signal or power connections. This often results in:
-
50/60 Hz hum or buzzing noise in audio systems
-
Measurement errors and unstable signals
-
Communication faults and data corruption
Isolation transformers eliminate ground loops by breaking the direct electrical connection between grounds, allowing systems to operate with independent reference potentials.
This is one of the most common reasons isolation transformers are installed in audio, control, and data systems.

Key Benefits at a Glance
Here’s a summary of the key advantages isolation transformers provide:
⭐ 1. Enhanced Safety
Reduces electric shock risk during operation, testing, and maintenance.
⭐ 2. Noise Reduction
Improves power quality and signal stability for sensitive electronics.
⭐ 3. Ground Loop Mitigation
Eliminates hum, interference, and unwanted circulating currents.
⭐ 4. Surge and Transient Buffering
Helps reduce the impact of voltage spikes and switching disturbances.
⭐ 5. Application Versatility
Suitable for medical, industrial, laboratory, data, audio, and telecom environments.
Common Applications
Medical and Healthcare Facilities
Isolation transformers are widely used in hospitals, operating rooms, and diagnostic equipment to meet strict safety standards such as IEC 60601, protecting both patients and medical staff.
Industrial Automation
They provide clean and isolated power for PLCs, sensors, control panels, and automation systems operating in electrically noisy environments.
Data Centers
Isolation transformers help stabilize power, reduce interference, and protect servers, networking hardware, and monitoring systems.
Telecommunications
They improve signal integrity and protect sensitive communication equipment from ground faults and electrical noise.
Audio and Video Systems
Isolation transformers are commonly used to eliminate hum and interference in professional audio, broadcast, and studio installations.
Choosing the Right Isolation Transformer
When selecting an isolation transformer, several technical factors should be considered:
-
Primary and secondary voltage ratings
-
Power capacity (kVA or VA rating)
-
Single-phase or three-phase configuration
-
Insulation class and temperature rise
-
Applicable certifications (UL, IEC, CE, etc.)
-
Installation environment (indoor, enclosure type, ventilation)
Consulting with a qualified electrical engineer or transformer manufacturer helps ensure the transformer is properly sized and configured for long-term reliability.
Conclusion
Isolation transformers are a cornerstone of safe, reliable, and clean electrical power delivery in modern power systems. By providing galvanic isolation, reducing noise, eliminating ground loops, and enhancing safety, they protect both equipment and people.
Whether used in medical electronics, industrial automation, data centers, or sensitive signal environments, isolation transformers play a vital role in building electrical systems that are efficient, stable, and trustworthy.

